How to open ports on your router
Speed can be everything online. Multiplayer gaming, interactive livestreaming, and file sharing will benefit from a faster connection. With port forwarding, you can make data transfer quicker and more efficient – if you know what you’re doing. Modifying your router can be intimidating, but it doesn’t take long to open ports on your router.
Malcolm Higgins
Dec 18, 2020 · 4 min read

So what is port forwarding? Why should you do it? And how do you open ports on your router?
The router and the network
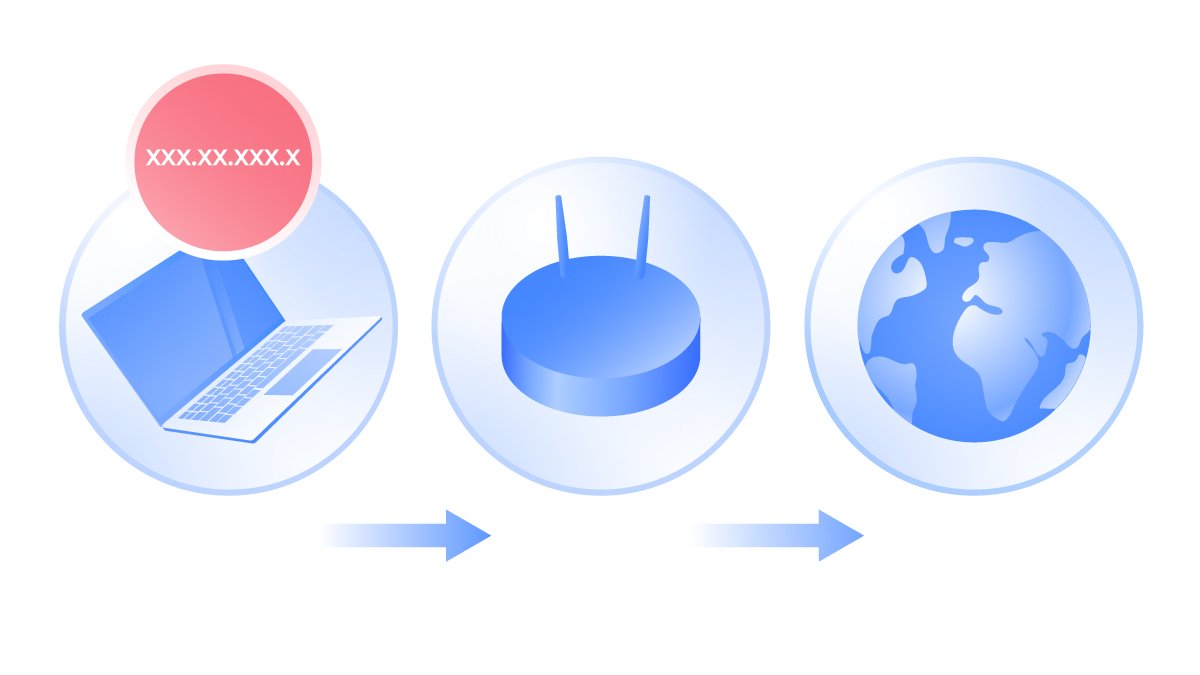
Before we jump into the specifics of ports themselves, it’s worth taking a moment to understand exactly how your router operates. Your router and any devices connected to it form a local network. The router is a gateway through which data travels in and out of that network.
Let’s imagine that you’re using a smartphone on your home Wi-fi. When you click on a blog article you want to read, you send a data “request” to your router. In turn, your router forwards the request to the blog's servers.
That server should then send the data you’ve requested back to your router, which will then pass it on to your smartphone. This all happens in a matter of milliseconds. But where do ports come in?
What are ports?
Ports are different channels through which your router sends and receives data. Your router has more than 65000 ports to use, which can be useful if you’re doing multiple things at once.
If you want to listen to Spotify and browse a webpage at the same time, your router will be receiving data from at least two servers simultaneously. It can be in contact with both servers at once because the data is moving through separate ports.
Certain programs and applications are designed to use specific ports. For example, whenever your network is sent data from an HTML page, the router will receive it via port number 80. Most of the time, this is a behind-the-scenes process and you won’t have to worry about it, but being able to modify how ports operate has its uses.
What is port forwarding?
Port forwarding involves telling your router that data received through a specified port should always be sent directly on to a certain device on the local network.
Normally, the router acts like a mail-sorting depot, examining the data it receives and deciding where it should be sent. This is also an opportunity for the router to block content it sees as dangerous or malicious, protecting the rest of the network from attacks and infections.
With port forwarding, you tell the router not to worry about screening or sorting through data arriving with a specific port. Instead, it can just send it on to a predetermined destination. This can speed up data transfers, and help make things like peer to peer sharing and online gaming easier.
How to set a static IP address
Before you can initiate port forwarding, you’ll need to set a static IP address for the device on the receiving end. Port forwarding only works if the final destination – your gaming computer, for example – always uses the same IP to identify itself.
To set up a static IP address, head to your router’s configuration page. You can find this by typing the router’s own IP into a browser. You’ll then have to enter a username and password. The login details should be available through your router provider, or with the box that it came in.
Once on the configuration page, look for an area in the settings called Static IP addresses, DHCP Reservations, or something similar (it may be contained in the Advanced Settings tab). Here you’ll find a list of the devices and servers on your network. Pick the one you want to use for port forwarding, and set the IP address to static.
Once you’ve made a note of the address, you can save your changes and move on.
Opening ports on your router
Having set a static IP address on the device you’re forwarding to, you can now open the port.
It’s worth noting that these steps will be slightly different for each type of router. The configuration pages and settings are unique to the specific brand and design, though they often share general similarities in layout and functionality.
- Navigate to your router’s configuration page by typing the router’s IP address into your browser.
- Find a settings tab for Ports, or Port Forwarding.
- Where indicated, input the number of the port you want to open.
- Where indicated, input the static IP address of the device you want the port to forward to.
- Save your changes to complete the process.
Can you open router ports with a VPN?
While opening ports on your router offers some potential benefits, it also exposes your devices to major risks online, leaving you vulnerable to malware infections. Browsing the internet with open ports removes the layer of security offered by your router; for that reason, NordVPN does not support port forwarding.
However, the port forwarding process does demonstrate the crucial role your router plays in secure network access. This one piece of hardware is the interface between any devices on a local network, and the rest of the internet.
For that reason, it’s worth taking time to protect your router properly. If you configure your router for NordVPN, you can shield multiple devices with layers of powerful encryption. Then, even if someone hacks your router, they won't be able to access the rest of the network, or any of the data passing through it.
NordVPN will protect not just your router, but the entire ecosystem of hardware connected to it.
Next-generation security is only a click away.